MuleSoft Technical Guides

Steps and Commands for RTF Installation on self managed kubernetes
Command Line Tools Installation:
Pre-requisites
- JDK
OpenJDK 11 > https://adoptium.net/temurin/releases/?version=11
OpenJDK 8 > https://adoptium.net/temurin/releases/?version=8
2. Install Chocolatey on Windows
a. Run a Powershell terminal as Administrator, then run Get-ExecutionPolicy. If it returns Restricted, then run Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned or Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process.
b. Install the Chocolatey Package Manager, a.k.a `choco`:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1’))
- Install kubectl
choco install kubernetes-cli –version=1.24.10 –allow-downgrade -y
- Install rtfctl
curl -L https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/runtimefabric/api/download/rtfctl-windows/latest -o rtfctl.exe
- Install Azure CLI MSI
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli-windows?tabs=azure-cli
Validate all tools are installed :
- kubectl version –client –short
- rtfctl version –help
- az
Azure KS Commands (Creating Kubernetes Cluster):
Create a resource group in Azure.
- CREATE CLUSTER
az aks create –resource-group <<resourcegroup>> –name <<clustername>> –node-count 2 –generate-ssh-keys –kubernetes-version 1.24.9 –node-vm-size Standard_DS2_v2
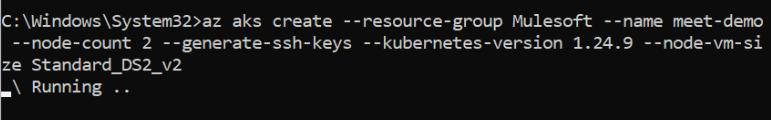
- Check created clusters
az aks list
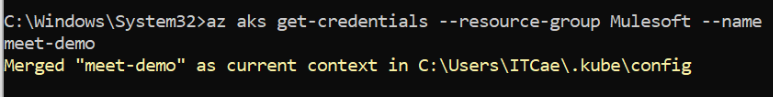
- GET CREDS (Get access credentials for a managed kubernetes cluster)
az aks get-credentials –resource-group <<resourcegroup>> –name <<clustername>>
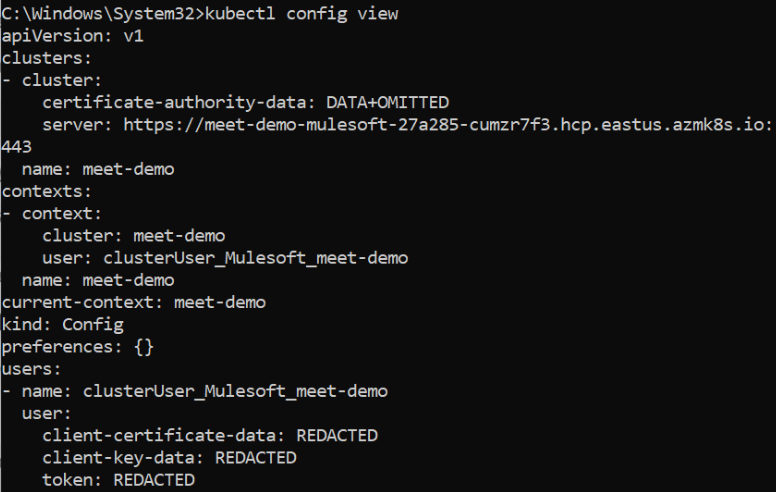
- View Kubernetes config
kubectl config view
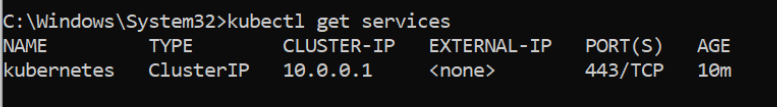
- Test connection to your cluster
kubectl get services
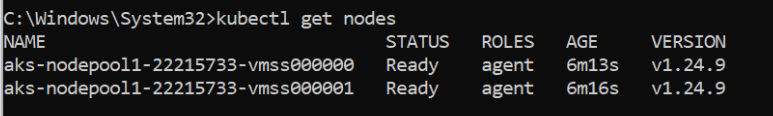
- GET NODES:
kubectl get nodes
Create Runtime Fabric Configuration in Runtime Manager
AND Get the Activation Code
RTF requires a separate license, so make sure you have a valid license
1.ACTIVATION CODE:
<<activation code>>
2.Validate the activation code:
rtfctl validate <<activation code>>
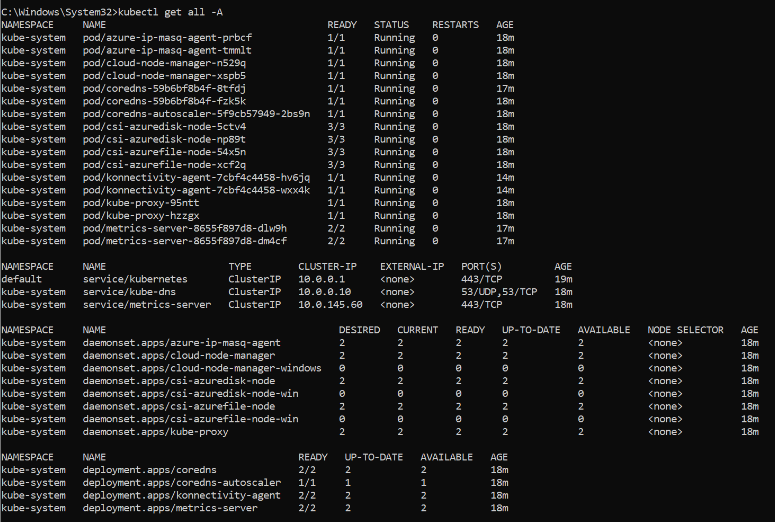
Examine existing components in Kubernetes cluster before RTF installation
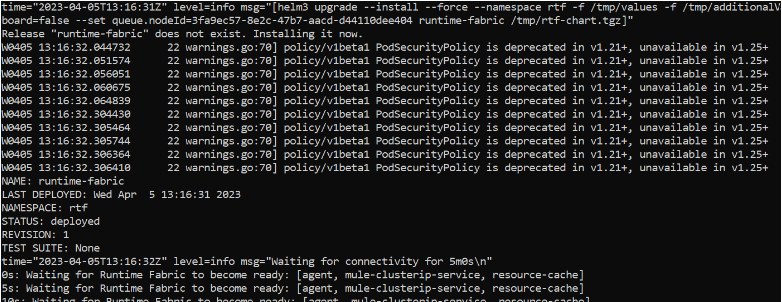
- Install the RTF:
rtfctl install <<activation code>>
- Check the RTF Status:
rtfctl status
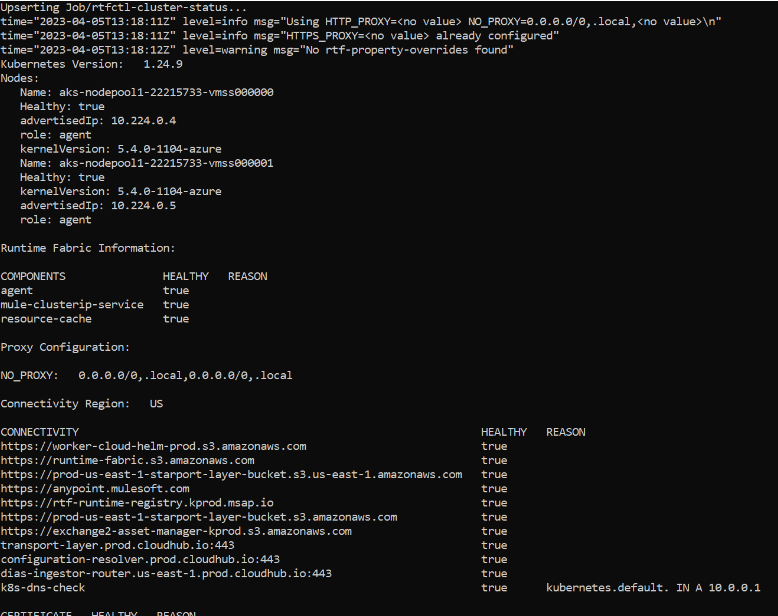
Now your RTF status should be activated in Runtime Manager
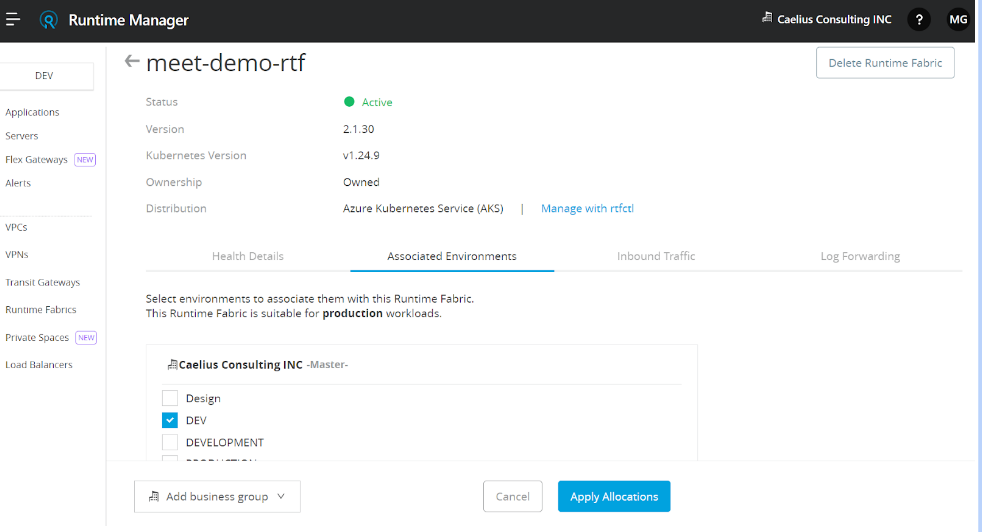
Apply associated Environment (as per requirement)
Insert Mule License Key
1.Encode Mule license key
Powershell command to encode the license
$BASE64_ENCODED_LICENSE=[convert]::ToBase64String((Get-Content -path “license.lic” -Encoding byte))
2.set /p encoded_text=<mulel.txt (In directory where encoded license present)
3.$encoded_text = Get-Content -Path “mulel.txt” -Raw (Run this command in Powershell)
4.rtfctl apply mule-license %encoded_text%
Now If you go to “Inbound Traffic”, you will see a Warning.
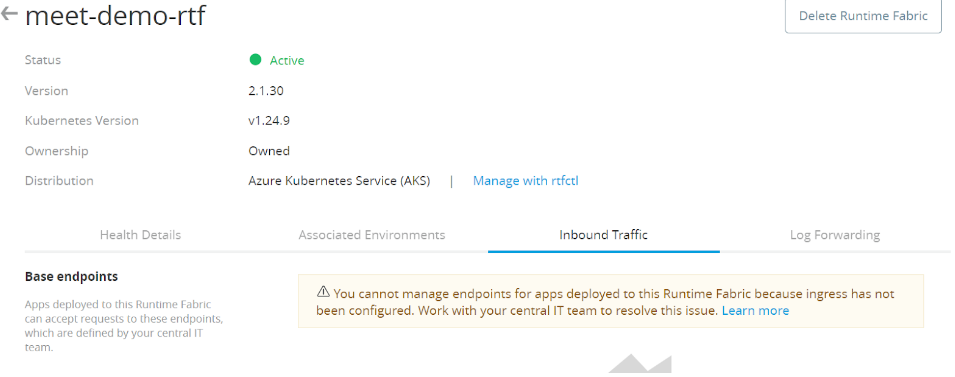
We need to configure Ingress in order to enable inbound traffic to our RTF cluster.
Define a custom ingress configuration
1. kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.1.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
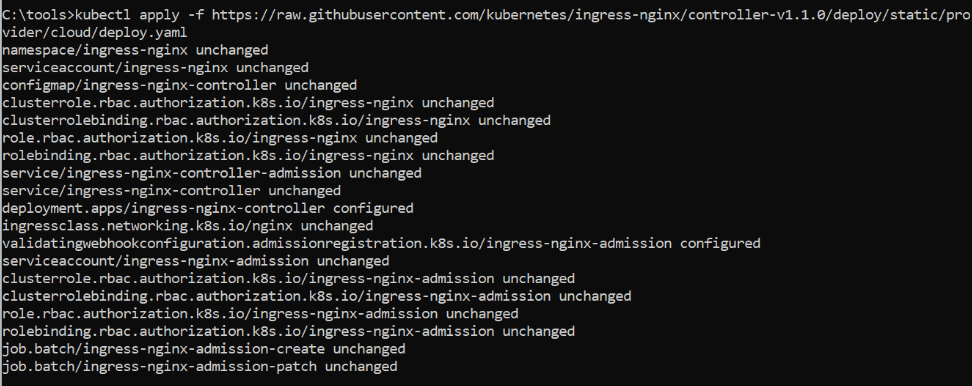
CREATE INGRESS CONTROLLER:
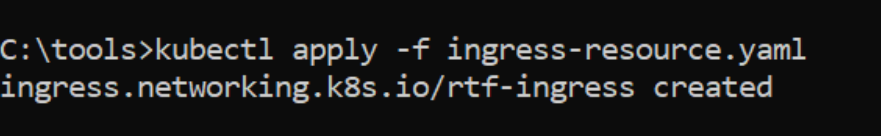
kubectl apply -f ingress-resource.yaml
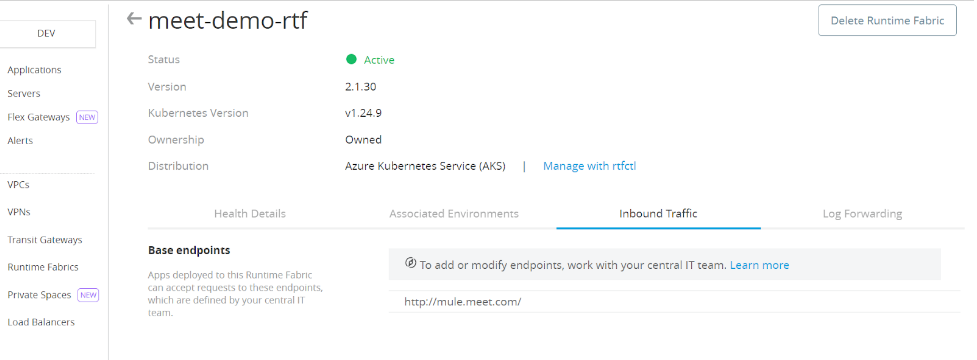
After configuring the ingress you will see the base endpoint as following:
Verify domains configured as base endpoints to runtime fabric
Deploy a Mule Application
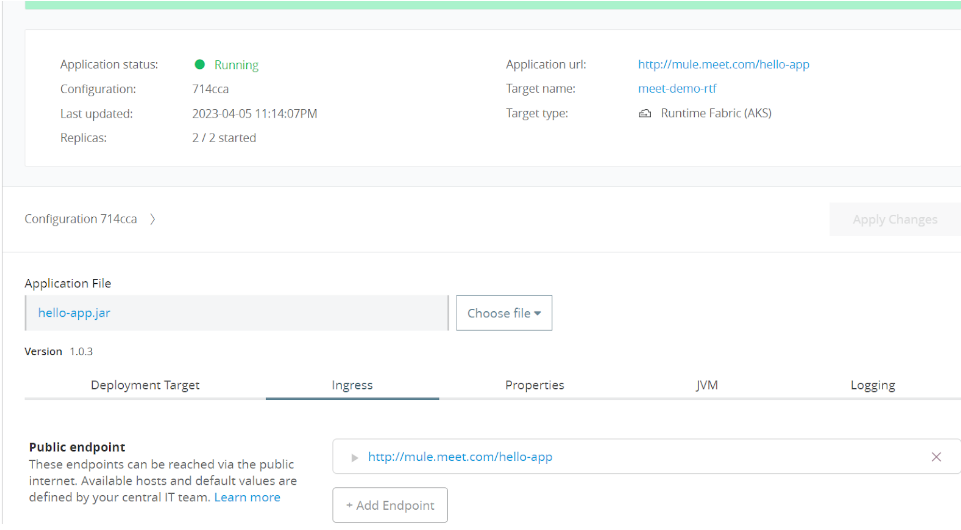
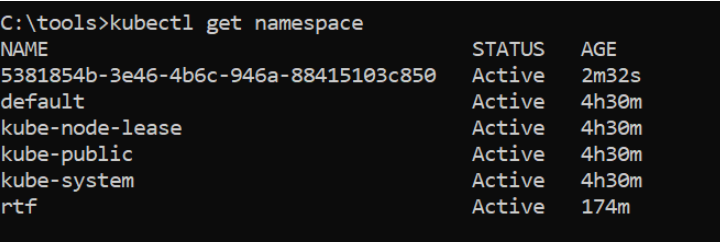
- After deploying app to check the namespace of mule apps
kubectl get namespace
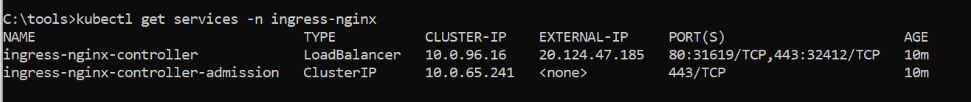
- To check services running on rtf
kubectl get services -n <<namespace>>
- To check pods running
kubectl get pods -n <<namespace>>
- GET EXTERNAL IPs:
kubectl get ingress -n <<namespace>>
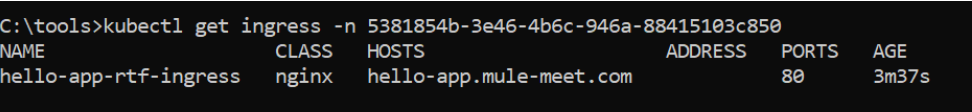
16. APPLICATION CALL: